Hi there, In this article, I have covered everything about Differential, its types, purpose of differential, construction, working and symptoms of bad differential, and many more.
You just got to know differential is of 4 types. To make this concept clear, let's start from the beginning.
What is Differential?
The differential is a mechanical component of a vehicle, which helps while turning by allowing the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner one. It creates a speed difference between two-wheel on the same line. Also, splits the toque coming from the propeller shaft.
There are 4 types of differential:
- Normal or Conventional Type
- Limit Slip Type
- Locking Type
- Torque Vectoring
Purpose of Installing Differential In An Automobile
While taking a turn or moving over any curved area. The inner and outer wheel of the vehicle moves at a different speed. The differential is designed in such a way so that it could perform this task easily. Here is the main 3 work of differential in an automobile.
- Transfer the engine torque coming from the propeller shaft to the road wheels.
- Differential split the torque received from the engine as per the wheel requirement.
- It varies the speed of the inner and outer wheels when taking a turn.
Types of Differential
As mentioned earlier differential is of 4 types, Normal, Limit Slip, Locking, and Torque Vectoring.
All of these have different properties:
- Normal Type - This is a normal one, it just creates a speed difference while turning between the two wheels.
- Limit Slip Type - When running in ideal road conditions, a limited-slip version acts just like a normal one. But, during hard cornering or heavy acceleration where an open differential could cause a tire to slip, a limited-slip diff prevents the normal amount of torque to go to the slipping tire.
- Locking Type - It has some extra components, like a combination of pressure late and a clutch plate inside the differential assembly. It just locks one side with the axle.
- It has a separate lever mechanism to operate as load and road conditions. Such types of differentials are used in heavy vehicles.
- Torque Vectoring - This is the most advanced version. It uses a combination of sensors and actuators to obtain data like (road surface, throttle position, steering system, etc.) and operates automatically by an electronic control module. Such types can be found in luxury segments vehicles.
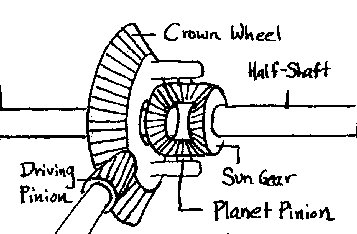
Differential Construction
Construction of Differential looks very complex but it is very simple to understand. There is not much difference between the front and rear wheel differentials.
In front wheels, the vehicle worm wheel is used whereas in case of rear-wheel drive crown ring gear is used. Apart from these, all the construction is the same.
As seen in the image, 2 side gears which are directly contented to wheels via axles and 2 plant pinions are there which are free to revolve in its own axis, they are connected via spyder pin. All these are arranged in a casing called differential housing.
All these are made of very hard and strong materials like iron.
Working Of Differential
The working of the differential is very simple to understand.
First, the power comes to the crown wheel via the propeller shaft.
- While Moving In Straight Line: During normal conditions or running in a straight line the full differential housing rotates and both the wheels rotate at the same speed.
- While Turning or Hard Cornering: While turning, the differential starts performing automatically. The ring gear drives the side gears, pinions, and axles as an assembly. At the point when the vehicle is turning, the wheels should move at various paces. Experiencing the same thing, the planet pinions turn concerning the crown wheel as they pivot the sun gears. This permits the speed of the crown gear to be conveyed unevenly to the two wheels. The construction of side gears and pinion gears allows the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner one. The side gears meshed with the pinion gears also rotate on their own centers.
Also: CRDI explained.
Different No. of Differential In Front, Rear, and All-wheel Drive Vehicles
You must be thinking, how many differentials does a car have?
The answer is 1,2 or 3. Different drive trains have different no of differential installed.
For example:
- For Front Wheel Drive - We use a transaxle gearbox. Which contain a single differential.
- For Rear Wheel Drive - We use a single differential, as all torque and power are transferred to the rear wheels. So, we use a rear differential.
- For All 4 wheel Drive - Here we use 2 differential. One for the front wheel and one for the rear wheels.
- For All Wheel Drive-In this case, 3 difference is used. One for the front, one for the rear, and one is fitted in between the front and the rear.
What will happen if you don't install Differential?
A vehicle if not equipped with a differential would result in the inner wheel spinning and the outer wheel dragging. As a result, It will damage tires and strain the entire drivetrain.
Symptoms of Bad Differential
There could be many symptoms, but I am mentioning a few of them which are very common.
- More tire wears on one side.
- Lubrication oil leakage
- Noisy Differential
Also: Definition of Automobile.


Comments
Post a Comment